This is the fifth post in a series about Reducing Gun Violence in the United States. The previous post described Laws, the Second Amendment, Litigation, and Obstacles to Research and Policy.
In this post, I’ll explore age-related firearm restrictions and child access prevention laws.
- For those who want to see the highlights without going through the data, skip right to the conclusions at the bottom of this post.
- The data in this post comes from several different sources, which I’ve linked in the references section at the bottom of this post for those who want to see the data for themselves or dive deeper.
Evidence for Age-Related Firearm Restrictions from Developmental Science
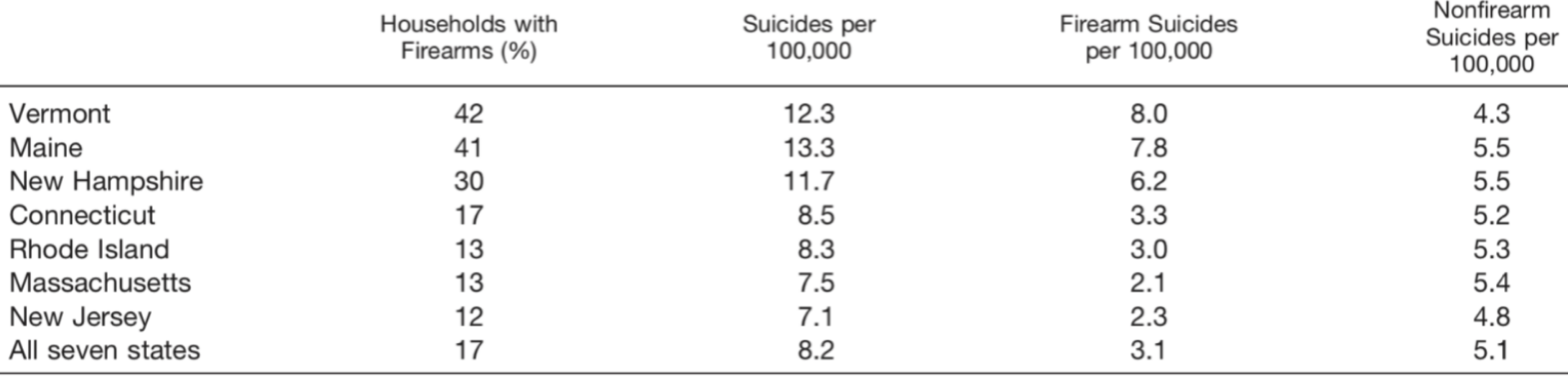
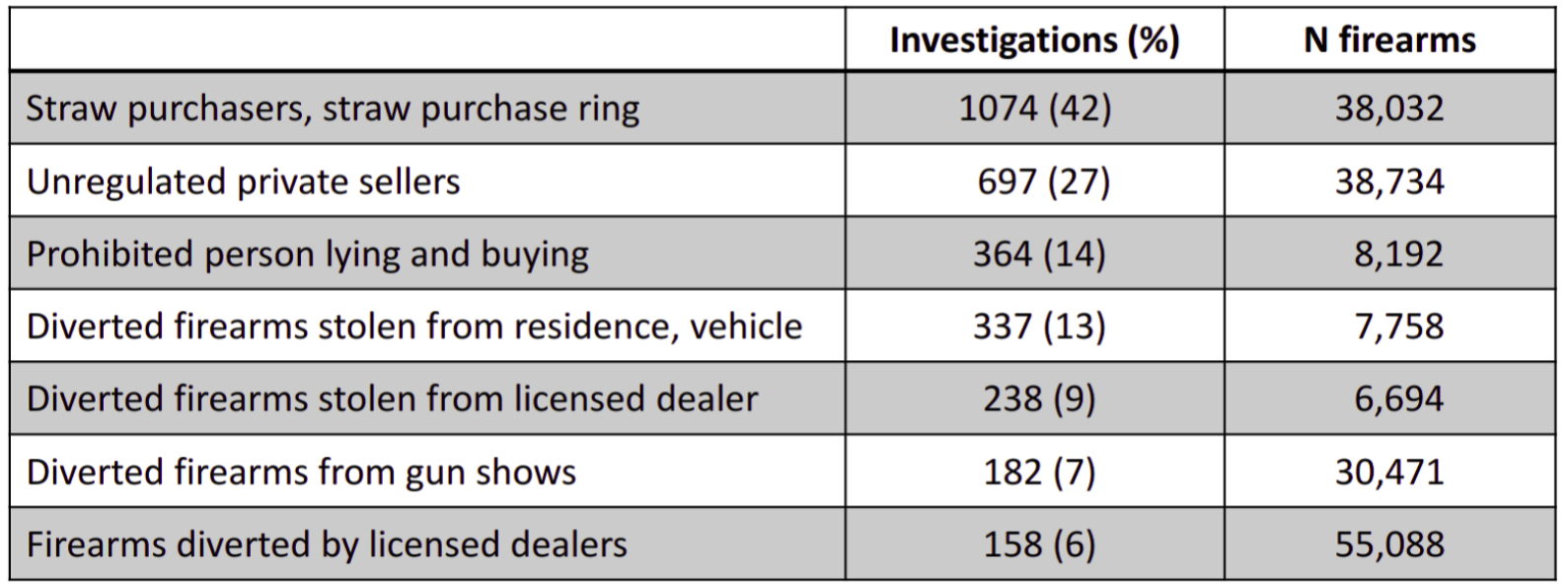
Federal Minimum Ages for Gun Purchases (source: Giffords Minimum Age)
In addition to the restrictions for owning firearms that we saw my previous post on gun laws, federal laws also include minimum ages for purchasing guns. For example:
- Long guns (examples include rifles or shotguns): 18 years
- Handguns: 21 years
Some states impose higher minimum age restrictions for purchasing guns.
Why do we have these restrictions? To answer that question, we need to look into what happens to people as they age from children to adults.
What’s going on during adolescence?
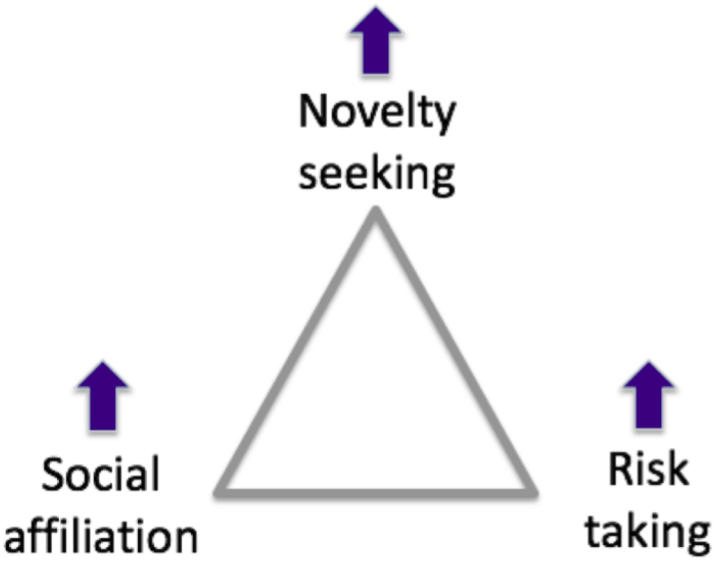
Three major changes occur during adolescence (source: Adolescent Maturity and the Brain)
- Increases in novelty-seeking, or looking for new, exciting experiences
- Increases in risk-taking: healthy risks like performing in concerts as well as unhealthy risks like using drugs
- Increases in social affiliation, like building groups of friends or social circles
Brain Development in Childhood through Adulthood (source: How does the teenage brain work)
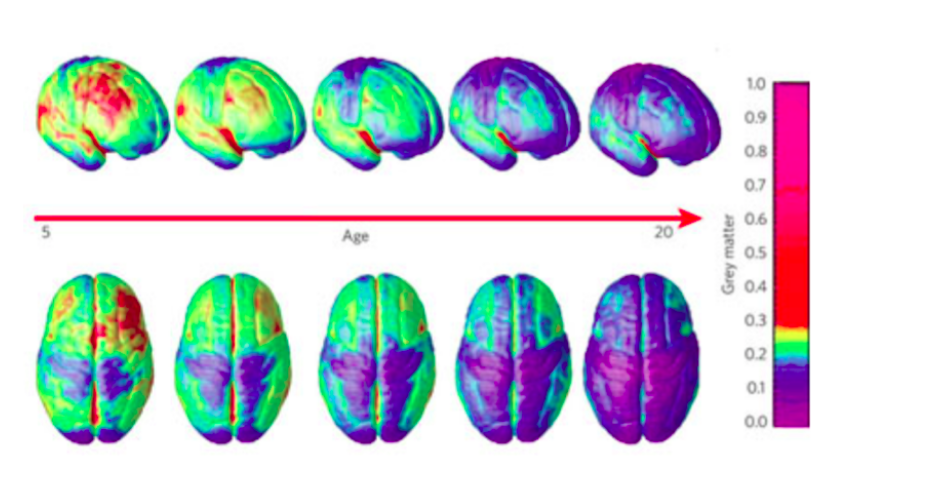
Current scientific understanding shows us that the human brain develops into the 20s and oftentimes well beyond these years. As seen above, the grey matter of the brain matures and gets denser as age 20 approaches (volume goes down but density goes up), generally starting from the back of the brain and moving to the front of the brain. The front of the brain, or the prefrontal cortex, is responsible for all kinds of logical behaviors such as delayed gratification, planning, and self-control. Put another way, those logical behaviors and skills develop more slowly than other skills that adolescents acquire. (source: Giedd)
Connectivity in the Brain over Time (source: Neurobiology of the Adolescent Brain)
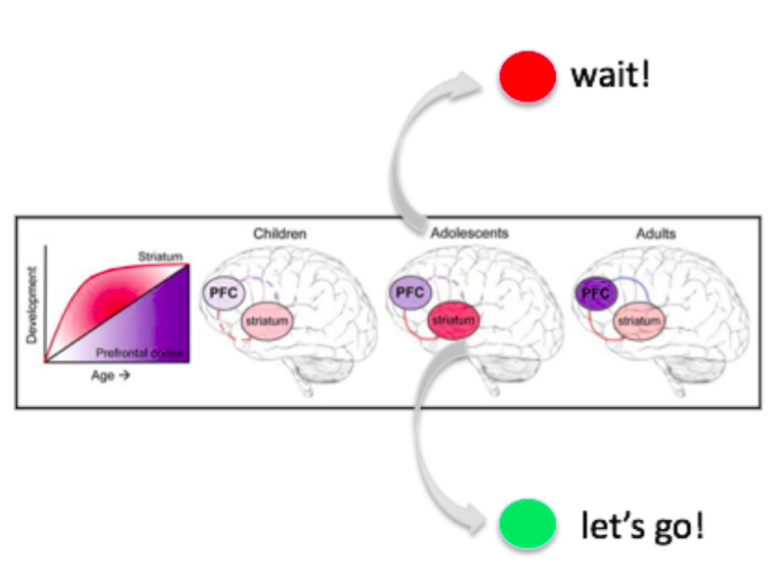
Another important area in the brain that is developing during adolescence is the striatum. The striatum regulates reward-seeking behavior and motivation. Something interesting to note about adolescent brain development is that the striatum matures much faster than the prefrontal cortex. The result of this is that the striatum is gets really good, quickly, at telling the adolescent brain “let’s go!” much sooner than the prefrontal cortex is getting good at saying “hmm, I’m not sure about that activity, let’s think about that a bit more”. In particular, the risks for misusing firearms show through clearly with more “let’s go!” thoughts and less “let’s think about that activity a bit more” thoughts.
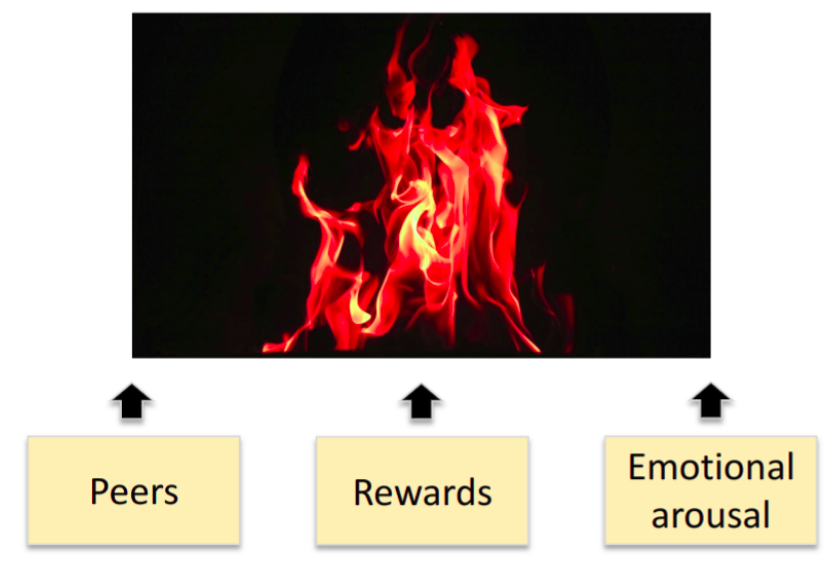
During adolescence, some decisions that people make look at lot like mature, adult decisions, while others look much less mature. Situations in which adolescents often make less mature, juvenile decisions are called hot cognitive decisions, which are those impacted by a person’s emotional state. Those situations often involve peers, rewards, and emotional arousal, which are the same influencers which can trigger poor decision-making (sources: Adolescents Less Mature, Understanding Adolescence).
In short, changes happening inside the brains of adolescents increase the likelihood of making risky or dangerous decisions that impact themselves and others.
Adolescents react more to stress (source: Stress Response)
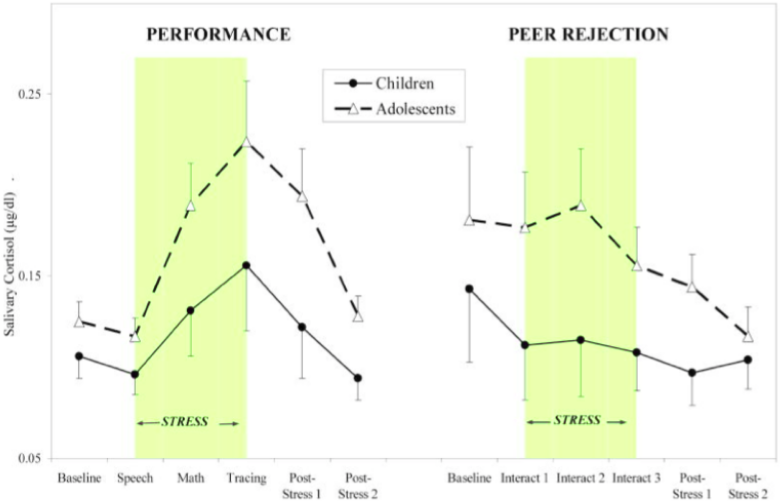
Adolescence is a critical time when any number of stressors impact our emotional lives. Things that happen during the adolescent years which add to this stress include: (sources: Regulatory Processes, Emerging Adulthood)
- Transitions in relationships, jobs, education, and living situations
- Less adult guidance and influence
- Greater access to alcohol and drugs
- Initial onset of common mental illness symptoms
- Highest rates of suicidal thoughts, plans, and attempts
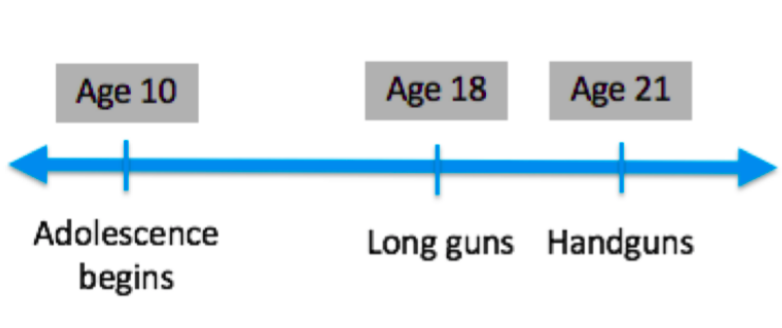
What does all of this have to do with firearms? Let’s go back to our picture of the minimum ages for purchasing firearms:

Age-related restrictions on firearm ownership are designed to prevent adolescents from mixing this risky period of transition with the lethality of firearms. The goal of these restrictions is to protect not only adolescents themselves but also the general public who might be put into harm’s way.
Child Access Prevention Laws
Child access prevention laws, or CAP laws, require gun owners to store firearms safely so that children cannot access them. Oftentimes, these laws have criminal penalties attached to them for gun owners who do not store their firearms in a safe manner.
Unfortunately, enforcement of these laws is spotty; often, they are not enforced until after someone is harmed by finding a gun stored unsafely in a house – law enforcement officers do not proactively monitor households for use of safe storage techniques.
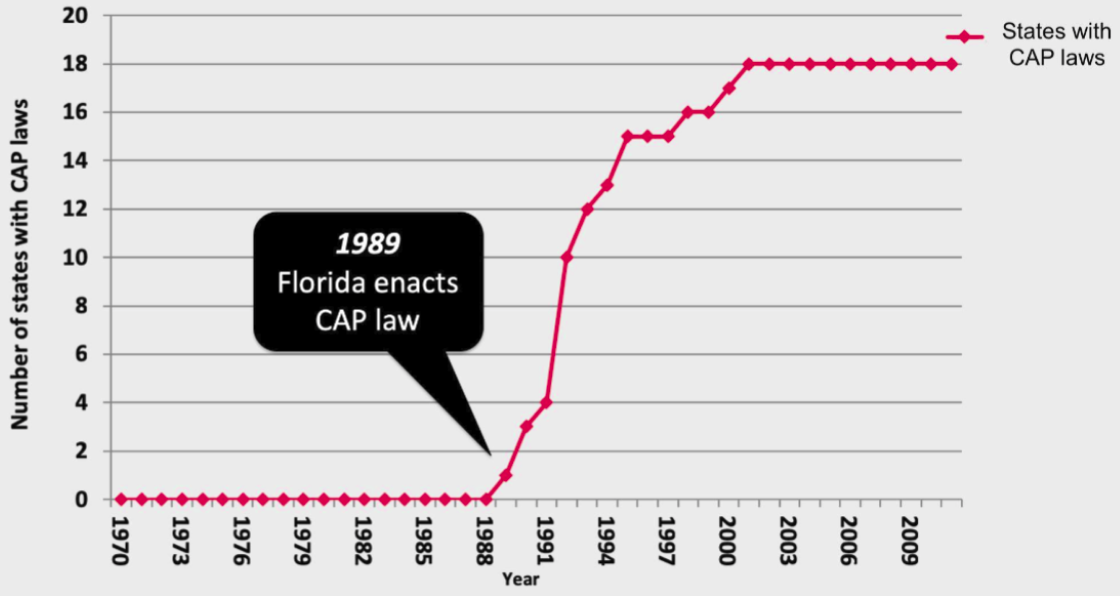
The first CAP law took effect in 1989 in Florida, and since then, 18 states and the District of Columbia have passed safe storage laws. Even more states passed laws which prevent “furnishing” guns to minors without explicitly requiring safe storage. However, no safe storage laws have been passed in the last decade.
An important question to ask is: do these safe storage laws actually work to protect children? Several studies looked at this question, and the results show that safe storage laws:
- reduce unintentional gun deaths
- may be more effective if penalties are felonies rather than misdemeanors
- are associated with a reduction in teen suicide
Conclusions
Evidence for Age-Related Firearm Restrictions from Developmental Science
- Adolescents brains mature at a rapid and uneven rate
- Brain areas which trigger reward-seeking behavior mature and take effect sooner than areas that are involved in planning and self-control
- Age-related restrictions on firearms are designed to prevent adolescents from making dangerous decisions with firearms when they are most at risk to do so
- Federal law creates age-based minimums for purchasing firearms based on this information
Child Access Prevention Laws
- Child access laws (or safe storage laws) exist in 18 states and the District of Columbia
- Though mostly unenforced until after an improper access
- CAP laws reduce unintentional gun deaths and are associated with a reduction in teen suicide
Next up: Violence, Alcohol, Drugs, and Guns
References
- Giffords Minimum Age – Giffords Law Center Minimum Age to Purchase & Possess report
- Adolescent Maturity and the Brain – a 2009 paper summarizing what is known about adolescent brain development
- How does the teenage brain work – a 2006 article about teenage brain development
- Neurobiology of the Adolescent Brain – a 2010 study focused on understanding how the brain is changing during adolescence relative to childhood and adulthood
- Adolescents Less Mature – a 2009 study showing that adolescents demonstrate adult levels of cognitive capability earlier than they show emotional and social maturity
- Understanding Adolescence – a 2012 report showing growing evidence pointing to the importance of changes in social and affective processing which are crucial to adolescent vulnerabilities
- Stress Response – a 2009 study showing heightened physiological stress responses in typical adolescents
- Regulatory Processes – a 2004 article highlighting clues from behavioral research on resilience to risks and assets, or vulnerabilities and protective factors in adolescence
- Emerging Adulthood – a 2014 study showing that individual differences entering adulthood can present risks for psychological disorders